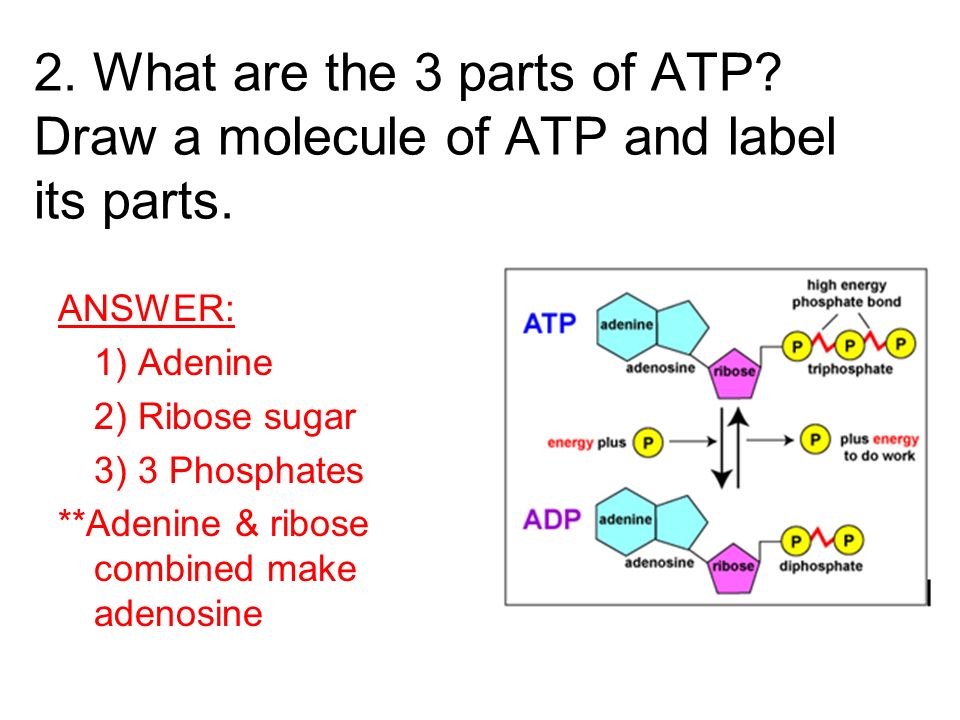
43 draw and label an atp molecule
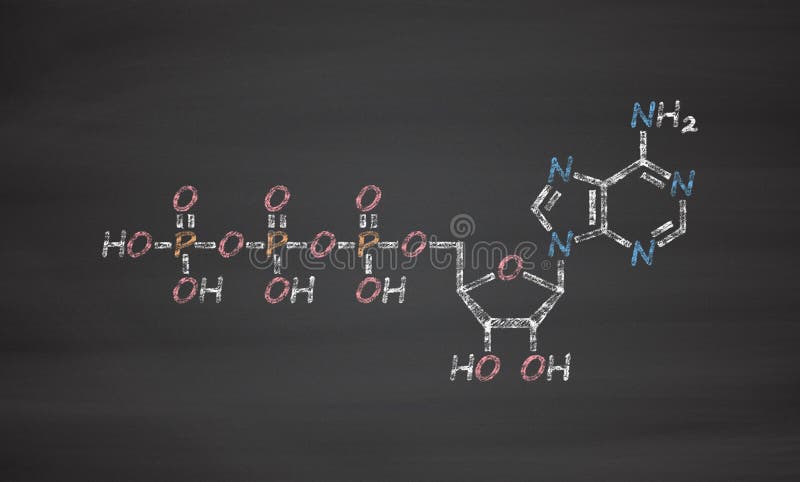
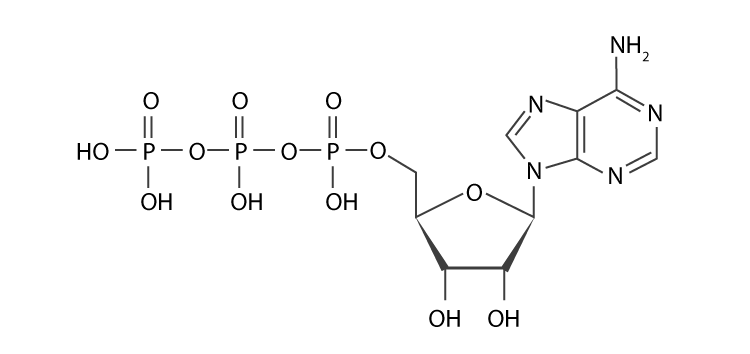
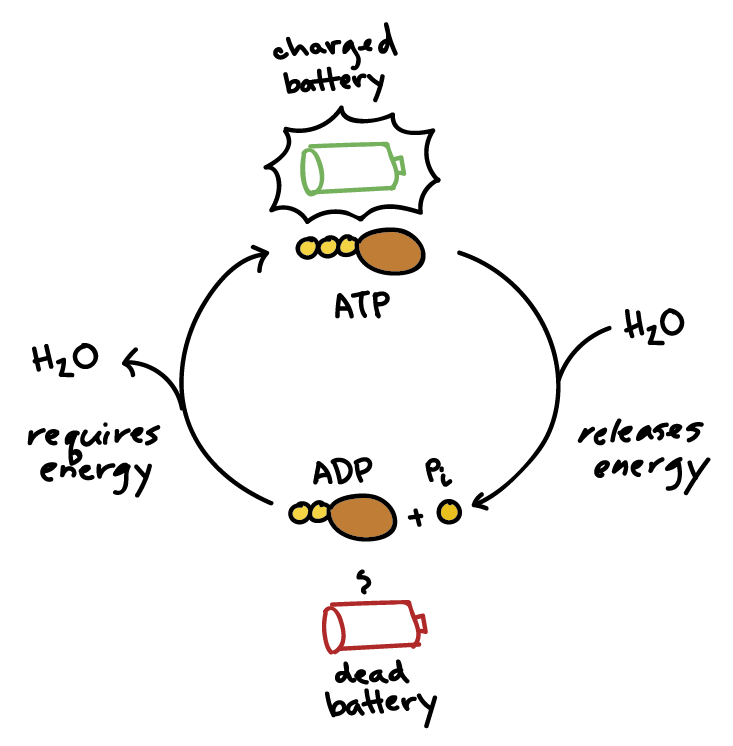
Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy ATP structure, ATP hydrolysis to ADP, and reaction coupling. ATP structure, ATP hydrolysis to ADP, and reaction coupling. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
Caffeine - Wikipedia Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine class. It is used as a cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional performance. Caffeine acts by blocking binding of adenosine to the adenosine A 1 receptor, which enhances release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Caffeine also increases cyclic AMP levels through nonselective …
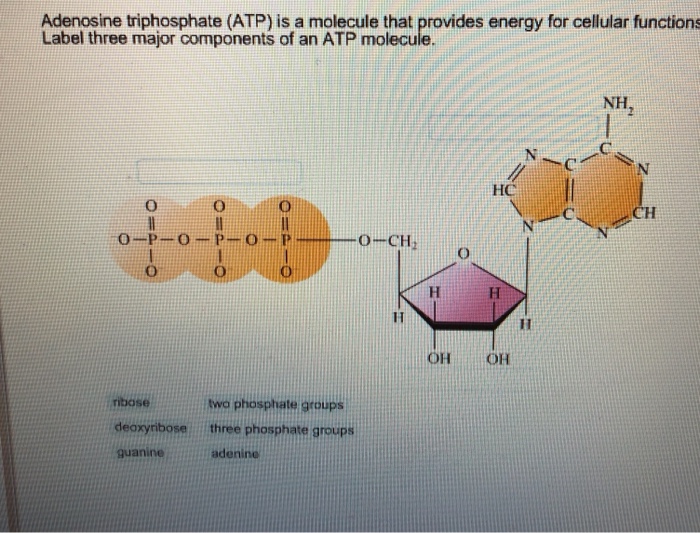
Draw and label an atp molecule
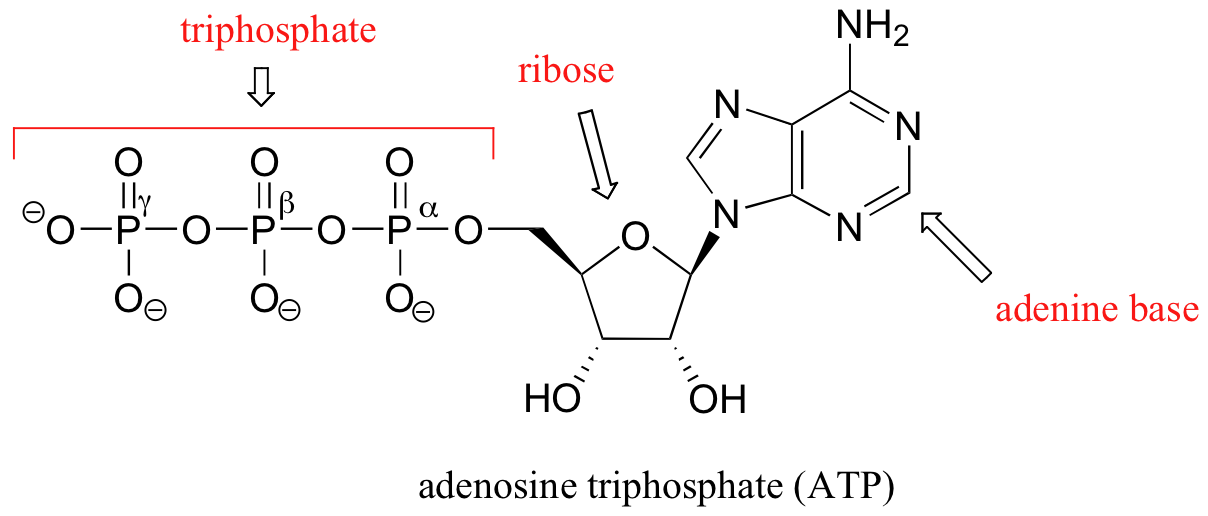
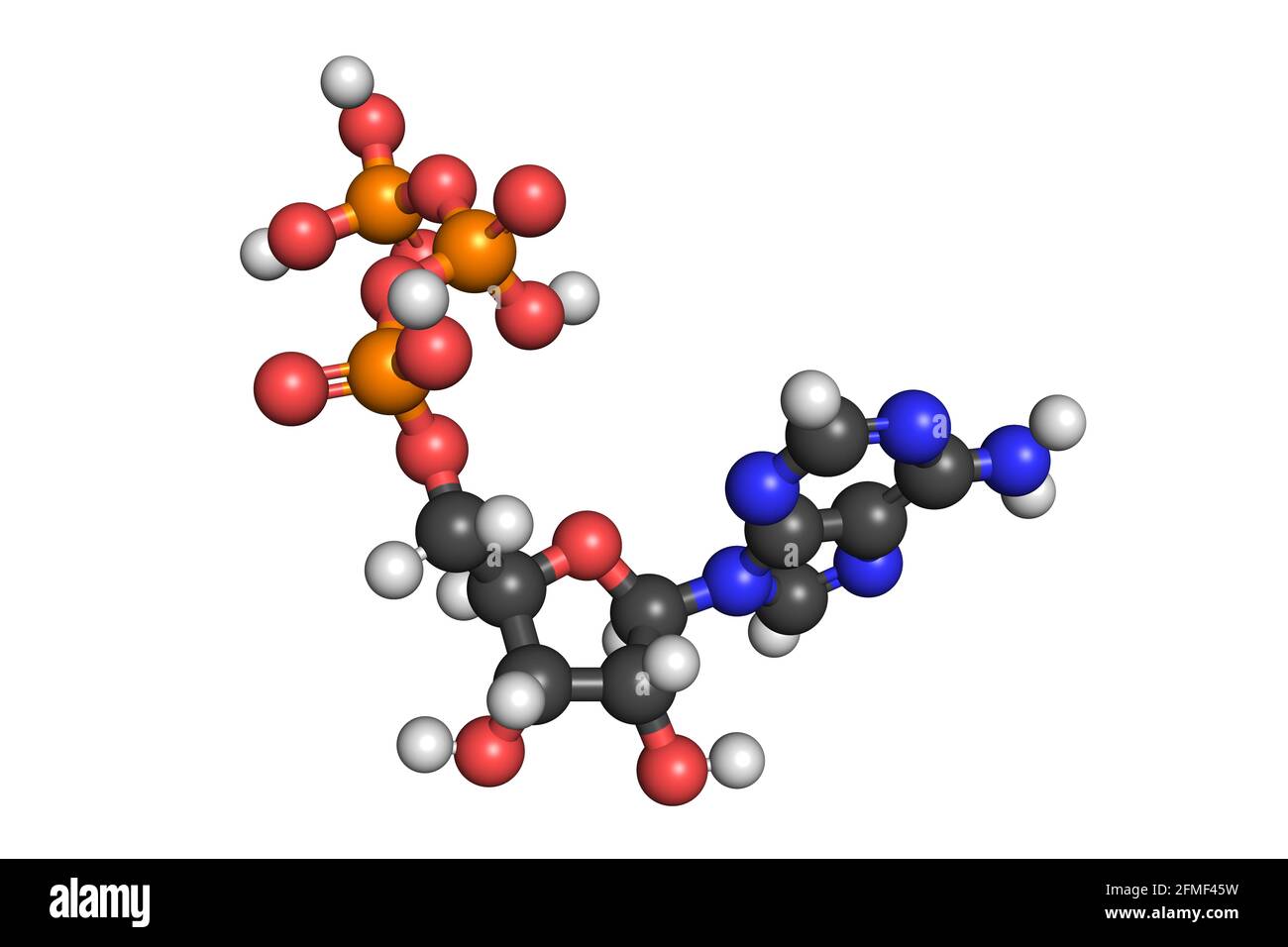
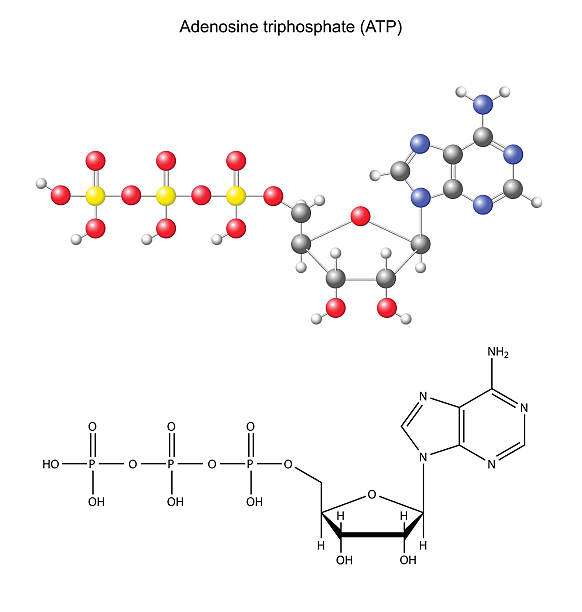
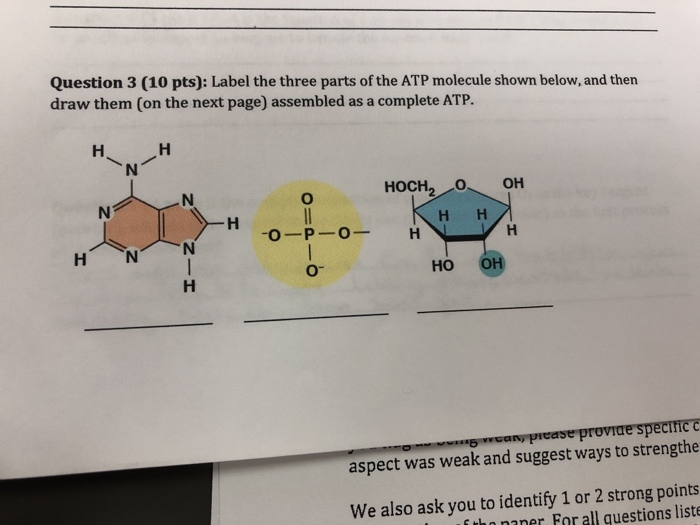
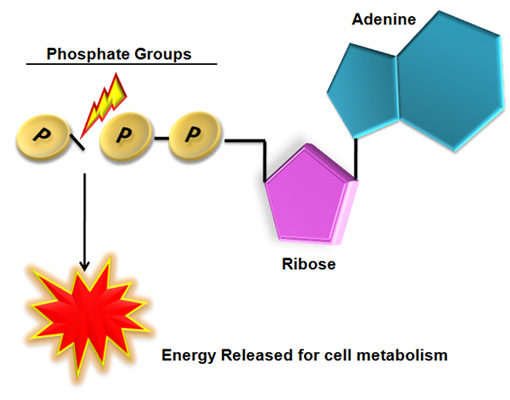
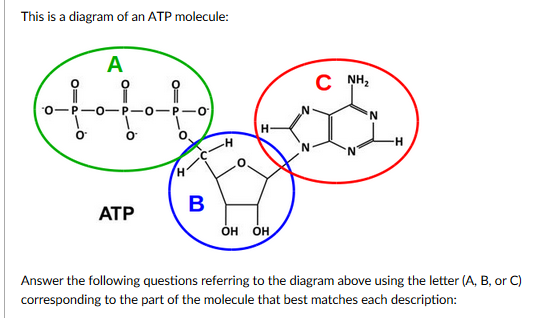
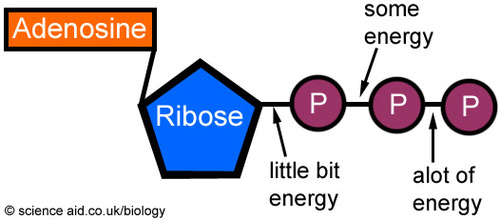
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture: ATP Diagram | Quizlet a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP. Tri. three. Di. two. ATP Cycle. a cycle that converts ADP into ATP & ATP releases energy and turns into ADP. ... 20% recombinants in the second cross, and 13% recombinants in the third cross. Draw a map placing the genes in the proper order and give the distance between each gene in map ... ATP - powering the cell - Cellular respiration - BBC Bitesize ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy-carrying molecule used in cells because it can release energy very quickly. Energy is released from ATP when the end phosphate is removed. Once ATP has ...
Draw and label an atp molecule. Krebs / citric acid cycle (video) | Khan Academy Let me draw it a little bit bigger. Let me draw a mitochondria here. So this is a mitochondria. It has an outer membrane. It has an inner membrane. If I have just one inner membrane we call it a crista. If we have many, we call them cristae. This little convoluted inner membrane, let me give it a label. So they are cristae, plural. What is the Structural Difference Between ATP and ADP An adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a high-energy molecule that stores energy. It is considered as the energy currency of life. All physiological mechanisms are powered by the energy stored in ATP. ATP can be found in both cytoplasm and nucleoplasm of the cell. More than 2 x 10 26 ATP molecules are daily produced inside the cell. ATP and ADP: Definition, Formation, Examples I ResearchTweet ATP to ADP Energy Release. As the ATP molecule consist of 3phosphate molecule and an adenine molecule, thus when ATP is converted to ADP, a phosphate molecule is lost in this process. The reaction can be written as ATP → ADP + P i. Thus, this reaction results in energy released which is used by the cells to perform the biological process. Solved 1) Draw a molecule of ATP, making sure to include and | Chegg.com 1) Draw a molecule of ATP, making sure to include and label the adenine, ribose, and three phosphates. 2) Discuss ATP's function as an energy molecule.
1 draw and label an atp molecule make sure to include 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Make sure to include the 3 parts. 2. What is the process called when a phosphate is added to the ADP molecule a. Photosynthesis b. Phosphorylation c. Permeability d. Precipitation 3. The metabolism (breakdown) of ________________ in the mitochondria provides the energy for the phosphorylation ofADP.a. ATP b. ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology - A Plus Topper Dec 04, 2019 · Sketch and Label the Diagram Question 1: Draw a neat and well-labeled diagram of the Chloroplast. Answer: Question 2: Draw a neat and well-labeled diagram of the apparatus you would set up to show that oxygen is given out during photosynthesis. Answer: See figure. Explain the Terms. Question: 1. ATP 2. Calvin Cycle 3. Free Energy 4. NADPH 5 ... Microbiological Examination of Foods: 7 Methods - Biology … An ATP molecule facilitates the formation of an enzyme- substrate complex which is oxidized by molecular oxygen to an electronically excited state. The excited state of the molecule returns to the lower energy ground state with the release of a photon of light and dissociates to release the enzyme luciferase again. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP.
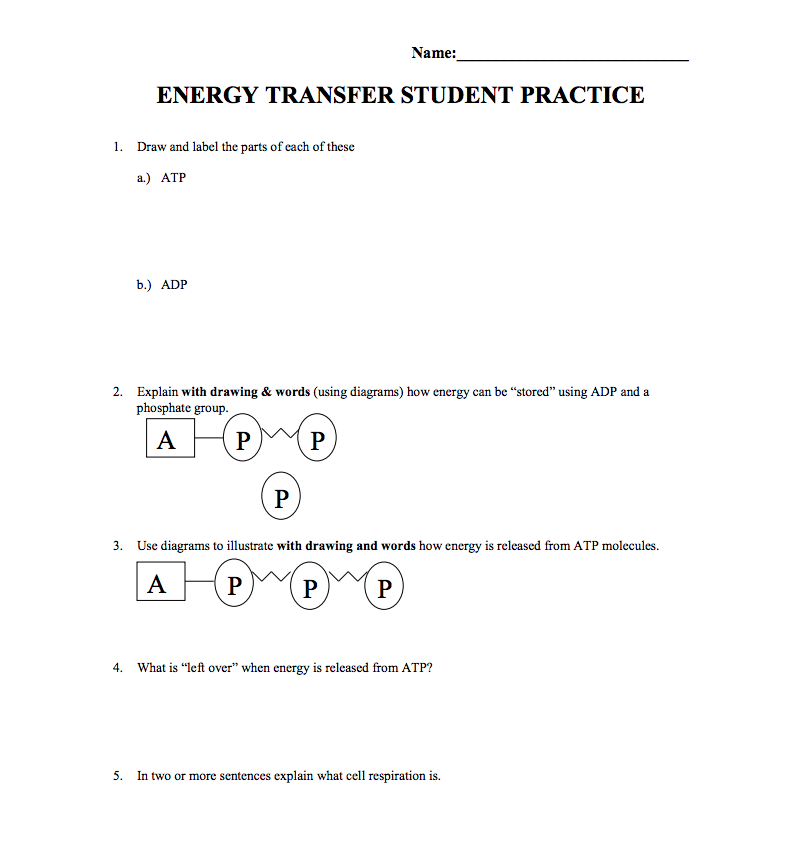
PDF Chemical Energy and ATP - bhsaicemarine.weebly.com Draw an ATP molecule. Label the adenine, ribose sugar, and the phosphate groups. 11. What does ADP stand for? _____ 12. What is the difference between ATP and ADP? _____ 13. When cells want to store up energy they will: add / delete (circle one) a phosphate group. 14. What is ATP like when it has all three phosphate groups? ... The GTP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules GTP Molecule. GTP (also known as guanylyl imidodiphosphate, guanosine-5'-triphosphate, or guanosine triphosphate) is a chemical compound (nucleotide) that is incorporated into the growing RNA chain during synthesis of RNA and used as a source of energy during synthesis of proteins. GTP is also essential to signal transduction in living cells ... Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram ... Draw the chemical structure of a glucose monomer associating with water through hydrogen bonds. On your diagram place a circle (O) around one hydrogen bond donor atom and label it donor'. On your diagram place a box () around one hydrogen... atp molecule Flashcards and Study Sets | Quizlet What are the three parts of an ATP mole… ATP chemical bonds (in phosphate groups) 1. Adenine... 2. Phosphate Groups... 3. Ribose 11 Terms Emmakhashim123 ATP ATP structure what catalysis ATP? hydrolysis of ATP nucleotide derivative and formed from a molecule of adenine, r… ATP hydrolase ATP --> ADP + Pi 17 Terms ky13la PLUS ATP
Learn About the 3 Main Stages of Cellular Respiration - ThoughtCo May 06, 2019 · ATP is ultimately produced by oxidative phosphorylation—the process by which enzymes in the cell oxidize nutrients. The protein ATP synthase uses the energy produced by the electron transport chain for the phosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule) of ADP to ATP. Most ATP generation occurs during the electron transport chain and ...
Answered: Draw and label a lipid bilayer… | bartleby Science Biology Q&A Library Draw and label a lipid bilayer containing the large mitochondrial trans-membrane protein complexes representing complex I, II, II, and IV, and ATP Synthase. Make two more of these drawings. Label the first one mitochondrial electron source and using a different ink color, indicate the source (s) of electrons.
Life Processes Class 10 Important Questions and Answers … Aug 03, 2020 · Draw a diagram of human respiratory system and label on it (i) Diaphragm and (ii) Larynx. (CCE 2014) Answer: Question 34. Three Kinds of Blood Cells. Red blood corpuscles, white blood corpuscles and blood platelets. Answer: Red Blood Corpucles (RBCs, Erythrocytes). Transport of oxygen and smaller quantity of CO 2. White Blood Corpuscles (WBCs ...
PDF Name: Date: 1)Draw an ATP Molecule and label all its parts. - Weebly 1)Draw an ATP Molecule and label all its parts. a)What does "ATP" stand for? 2)What is ATP used for in a cell? Big concept, not specifics… 3)How do you get energy out of an ATP molecule? Either diagram it or write it out in a sentence or two. 4)How do you store energy in an ATP molecule?
Biochemistry Questions and Answers | Homework.Study.com Each molecule of hemoglobin has four Fe atoms. Explain how you would use the radioisotope Fe-59 (half-life = 46 days) to show that the iron in a certain food is converted into hemoglobin. ... View Answer. Draw the reaction of 5,5-dimethoxyhexanal with lithium aluminum hydride. View Answer. Draw the Cleland notation for bisubstrate reactions ...
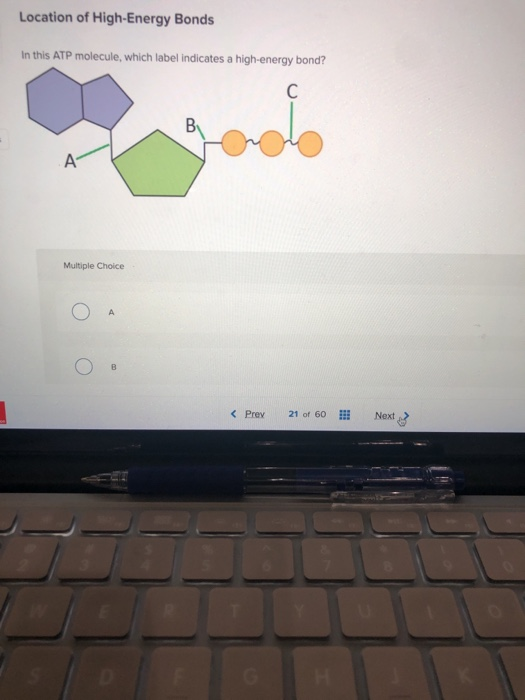
Draw the structure of ATP molecule. Label the high energy bonds ... Draw the structure of ATP molecule. Label the high energy bonds.\( P \)W📲PW App Link - 🌐PW Website -
Draw and label an ATP model please - Brainly.com Answer: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of ATP.
Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing - Chegg Question: 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. Explain why glucose is important. groups groups 4. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? 5. Where does glycolysis occur? = 6.
Pharmacology Questions and Answers | Homework.Study.com Label each compound as chiral or achiral. ... Is ATP optically active? It's IUPAC name is (((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl) methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl) phosphono hydrogen phosphate. ... Draw the B r F 5 molecule, with correct chirality, by placing atoms on the grid and connecting them with bonds. ...
Chapter 6: Photosynthesis | Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class … (c) ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) stores energy in the cells. (d) Glucose is the first form of food substance produced during photosynthesis. (e) The carbon dioxide dissolved in water. (f) Stroma is the part of chloroplast where dark reaction of photosynthesis takes place. Question 2. Given below are groups of terms.
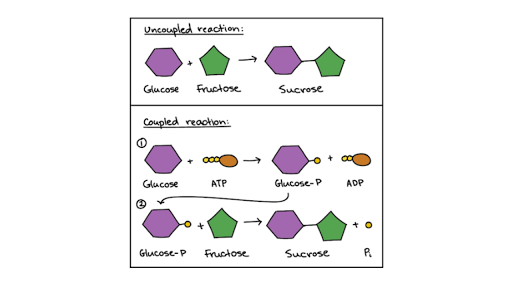
How does atp store and release energy? | Socratic This occurs when a molecule of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) uses the energy released during cellular respiration to bond with a third phosphate group, becoming a molecule of ATP. So the energy from cellular respiration is stored in the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups of ATP. When the cell needs energy to do work, ATP loses its 3rd ...
Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain ... ATP is a form of nucleotide structure which is mainly responsible for providing or driving the energy present in stored form from one point to another, through various chemical reactions. ( Metabolic pathways). It is mainly composed of three parts: A nitrogenous base, adenine, The sugar molecule, ribose. A chain of three phosphate group.
Photosynthesis: ATP and ADP Cycle - bealsscience ATP is one of the most important compounds inside a cell because it is the energy transport molecule. ATP (Adenosine TriPhosphate) is considered a transporter of energy because when one of the phosphate groups is broken off, turning it into Adenosine DiPhosphate (the Tri means 3 phosphate groups, the Di means 2 phosphate groups).
Bell Ringer 1 Draw and label the ATP - slidetodoc.com Bell Ringer: 1. Draw and label the ATP Molecule 2. What does ATP stand
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules The Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. For 3-D Structure of this image using Jsmol Click here
CR Study guide.pdf - 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule.... Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy (including the enzyme responsible). 2. Why is ATP important? ATP is important because it supplies energy for our cells; without it we would not have the energy to grow, move, etc.Ribose PAdenine P
PDF worksheet chemical energy and ATP - Frontier Central School District 5. Identify the parts of an ATP molecule below: (Label adenosine, ribose, and phosphate molecules) 6. How is energy stored in the ATP molecule? 7. What happens to the ATP molecule when a phosphate group is removed ? (what does it turn into?) 8. Draw a diagram below showing the cycle of ATP and ADP below (see Figure 4.2 on page 101) 9.
Maharashtra Board Class 10 Science Solutions Part 2 Chapter 2 … Jan 13, 2021 · Draw a neat diagram of the structure of chromosome and label the parts: (a) Centromere (b) p-arm (March 2019) Answer: Question 2. Sketch and label the diagram to show ATP – the energy currency of the cell. Answer: Question 3. Mitochondria and Krebs cycle: Answer: (a) Which co-enzymes are shown in the diagram? Answer:
ATP - Energy Currency of the Cell - Structure and its Functions - BYJUS The ATP molecule was discovered in the year 1929 by German chemist Karl Lohmann. Later in the year 1948, Scottish biochemist Alexander Todd was the first person to synthesized the ATP molecule. ATP - the energy-carrying molecules are found in the cells of all living things. These organic molecules function by capturing the chemical energy ...
ATP - powering the cell - Cellular respiration - BBC Bitesize ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy-carrying molecule used in cells because it can release energy very quickly. Energy is released from ATP when the end phosphate is removed. Once ATP has ...
ATP Diagram | Quizlet a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP. Tri. three. Di. two. ATP Cycle. a cycle that converts ADP into ATP & ATP releases energy and turns into ADP. ... 20% recombinants in the second cross, and 13% recombinants in the third cross. Draw a map placing the genes in the proper order and give the distance between each gene in map ...
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture:






















Post a Comment for "43 draw and label an atp molecule"