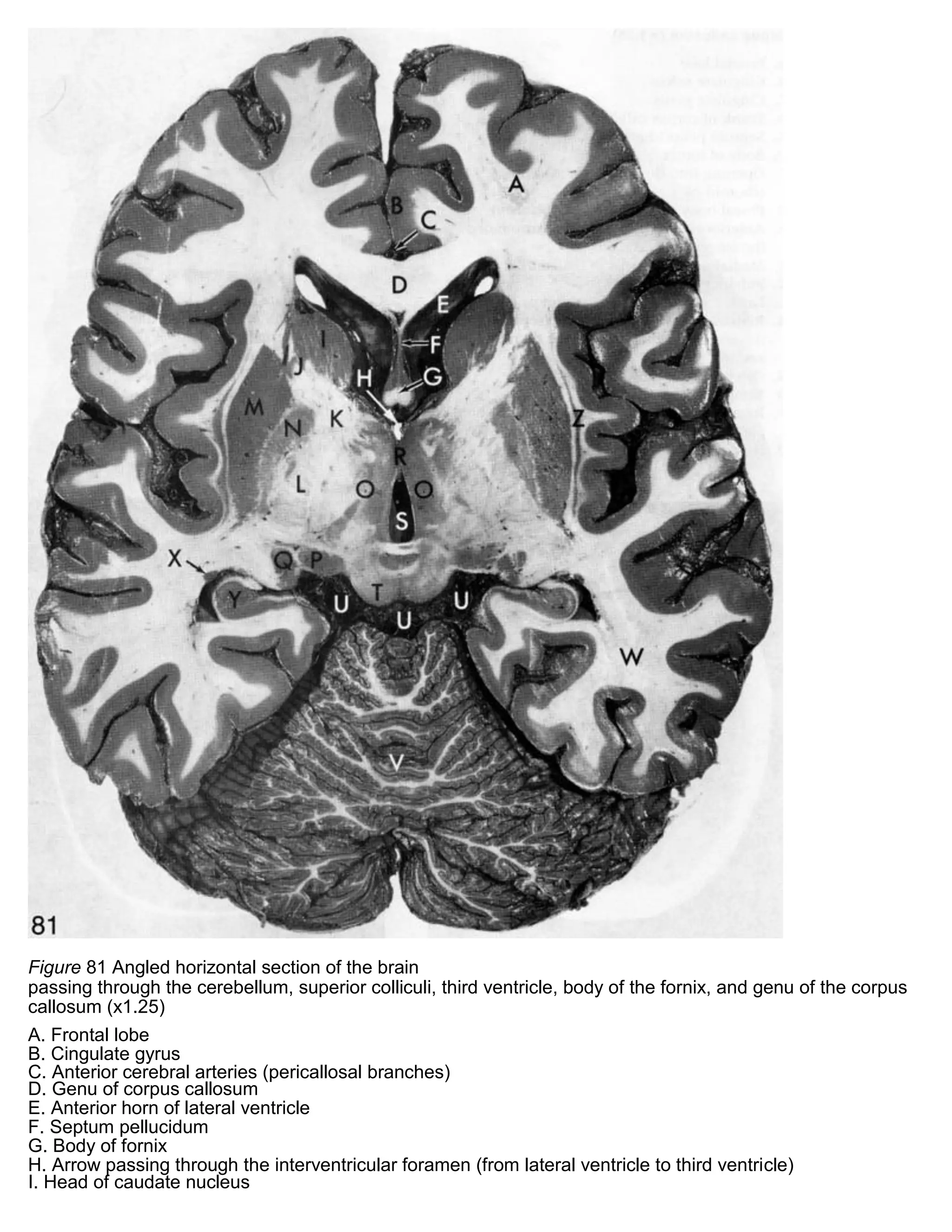
39 cerebellum labelled
Neuroanatomy, Cerebellum - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The cerebellum is a vital component in the human brain as it plays a role in motor movement regulation and balance control. The cerebellum coordinates gait and maintains posture, controls muscle tone and voluntary muscle activity but is unable to initiate muscle contraction. Damage to this area in humans results in a loss in the ability to control fine movements, maintain posture, and motor ... Ex Vivo Characterization of a Novel Iodine-123-Labelled ... - Hindawi 25. jouluk. 2014 · Ex Vivo Characterization of a Novel Iodine-123-Labelled Aminomethylchroman as a Potential Agonist Ligand for SPECT ... where the observed binding in the D 2/3 receptor-rich striatum was slightly higher than that in the cerebellum 30 min to 4 h p.i. Storage phosphor imaging experiments, however, did not show specific D 2/3 ...
Cerebellum | Description, Anatomy, & Functions | Britannica the cerebellum integrates nerve impulses from the labyrinths of the ear and from positional sensors in the muscles; cerebellar signals then determine the extent and timing of contraction of individual muscle fibres to make fine adjustments in maintaining balance and posture and to produce smooth, coordinated movements of large muscle masses in …

Cerebellum labelled
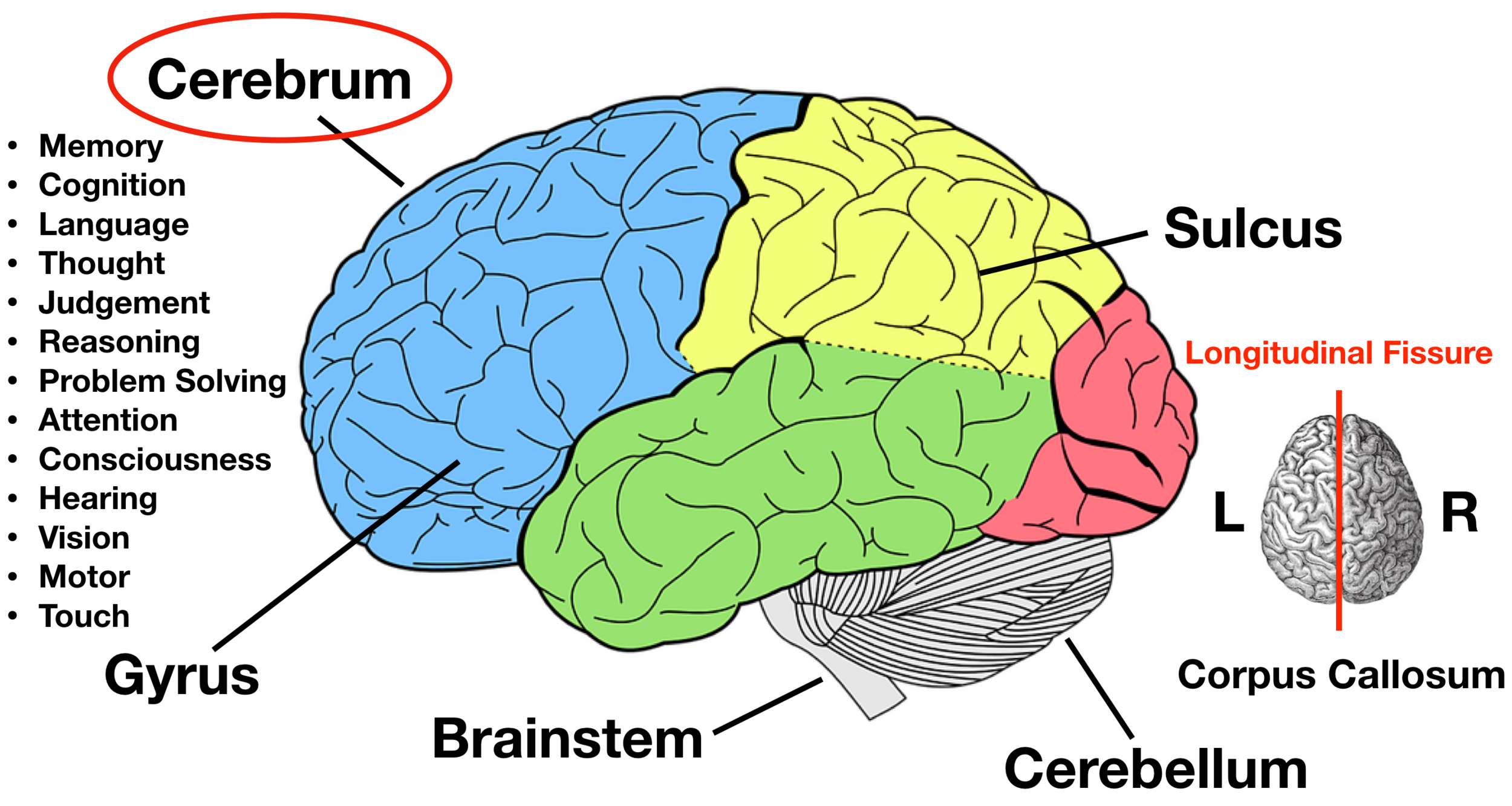
Cerebellum: Definition, Location, and Functions - Verywell Mind The cerebellum (which is Latin for "little brain") is a major structure of the hindbrain that is located near the brainstem. The cerebellum is the part of the brain that is responsible for coordinating voluntary movements. It is also responsible for a number of functions including motor skills such as balance, coordination, and posture. Nervous System - Label the Brain - TheInspiredInstructor.com Choose the correct names for the parts of the brain. ( 9) This brain part controls thinking. (10) This brain part controls balance, movement, and coordination. (11) This brain part controls involuntary actions such as breathing, heartbeats, and digestion. (12) This part of the nervous system moves messages between the brain and the body. The Cerebellum - Structure - Position - Vasculature - TeachMeAnatomy The cerebellum, which stands for "little brain", is a structure of the central nervous system. It has an important role in motor control, with cerebellar dysfunction often presenting with motor signs. In particular, it is active in the coordination, precision and timing of movements, as well as in motor learning.
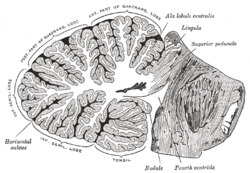
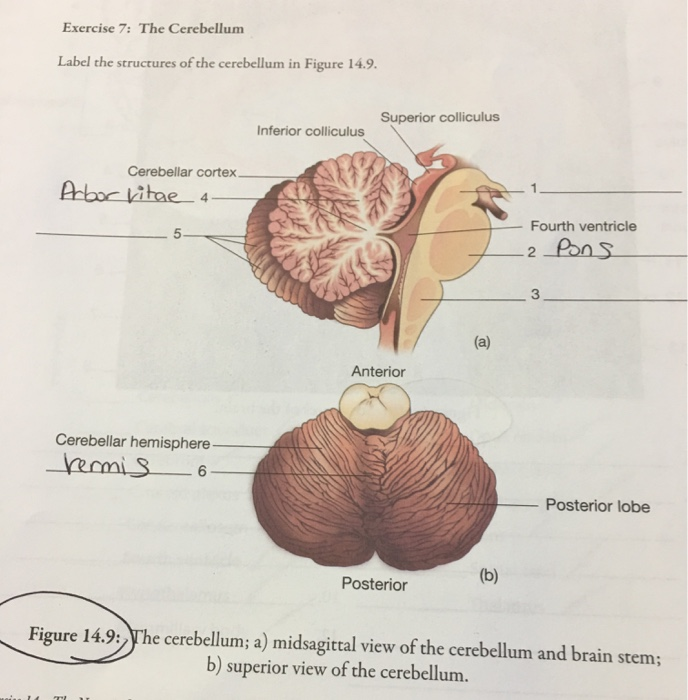
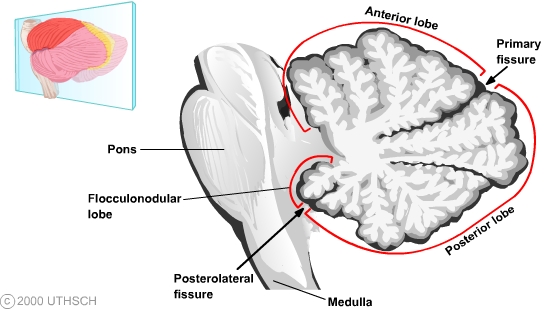
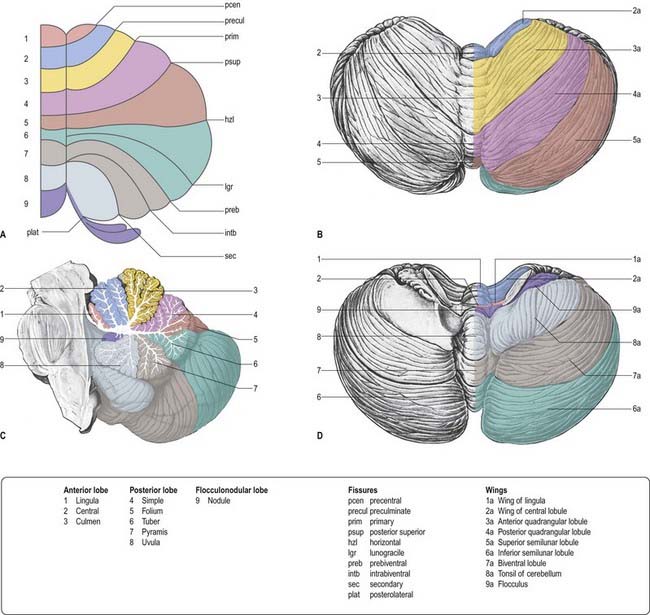
Cerebellum labelled. 11.5A: Parts of the Cerebellum - Medicine LibreTexts the cerebellum as in the neocortex. Based on surface appearance, three lobes can be distinguished in the cerebellum: the flocculonodular lobe, anterior lobe (above the primary fissure), and the posterior lobe (below the primary fissure). Key Terms granule cells: An extremely small type of neuron that is the the smallest cell found in the brain. Hemisphere of cerebellum - e-Anatomy - IMAIOS Anatomically, the cerebellum can be divided into three lobes. The anterior lobe-in front of the primary fissure-contains lobules I-V [H] of hemisphere of cerebellum (Larsell). These are labelled as Vicingulum lingulae, Ala of lobuli centralis and Anterior quadrangular lobules of hemisphere of cerebellum, as per the classic nomenclature system. Cerebrum: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment - Verywell Health The cerebellum is the second largest part of the brain and it is involved in coordinated movement, posture, and balance. The cerebral cortex has a series of folds that allow for a larger surface area to house more gray matter and its powerful information processing. 1. Each groove or low point is known as a sulcus. The Cerebellum: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections The Cerebellum: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections - YouTube 0:00 / 28:28 The Cerebellum: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections 158,414 views Sep 9, 2015 The gross features of...
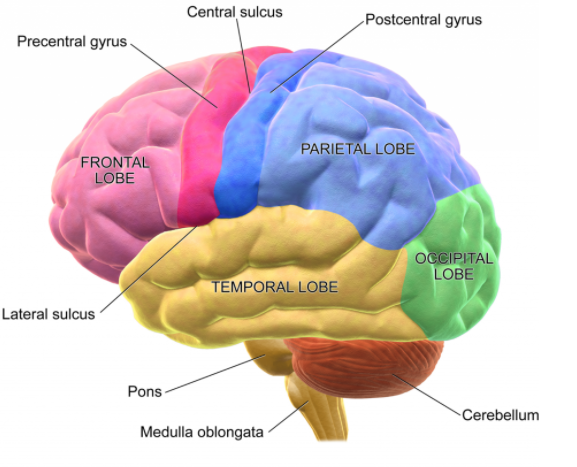
Anatomy of the Cerebellum and its Function - ThoughtCo In Latin, the word cerebellum means little brain. The cerebellum is the area of the hindbrain that controls movement coordination, balance, equilibrium and muscle tone. Like the cerebral cortex, the cerebellum is comprised of white matter and a thin, outer layer of densely folded gray matter. Cerebellum Facts, Function, Location, and Disorders - Healthline The cerebellum can be found just below your cerebrum and behind the upper portion of your brain stem. This is the area at the base of your skull where your head meets your neck. The cerebellum... Cerebellum (Section 3, Chapter 5) Neuroscience Online: An Electronic ... The cerebellum("little brain") is a structure that is located at the back of the brain, underlying the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex (Figure 5.1). Although the cerebellum accounts for approximately 10% of the brain's volume, it contains over 50% of the total number of neurons in the brain. Anatomy of the cerebellum | Osmosis The word cerebellum translates to little brain. Not because it's the brain of a tiny animal or baby, but rather because of the fact that the cerebellum looks like a smaller version of the human cerebrum.. Very simply, the cerebellum assists with coordinating and adjusting voluntary movement.It plays a major role in posture, balance, maintenance of muscle tone and coordinating skilled ...
Cerebellum: What It Is, Function & Anatomy - Cleveland Clinic What is the cerebellum? Your cerebellum is a part of your brain located at the back of your head, just above and behind where your spinal cord connects to your brain itself. The name "cerebellum" comes from Latin and means "little brain." For centuries, scientists believed your cerebellum's job was to coordinate your muscle movements. Cerebellum Function, Location & Anatomy | What is the Cerebellum ... The cerebellum is the part of the brain located at the back, inferior to the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. The cerebellum has many important functions in the body. It... Shared and distinct transcriptomic cell types across ... - Nature 1. marrask. 2018 · This type is labelled by tamoxifen induction at embryonic day (E) 18 of Nkx2.1-creERT2 mice (Extended Data Fig. 8) and was isolated previously 36 from the same Cre line (Extended Data Fig. 12a–c). Histology of cerebrum and cerebellum - SlideShare 1. HISTOLOGICAL FEATURES OF CEREBRUM CEREBELLUM Prof.J.Anbalagan. 2. CEREBELLUM. 3. CEREBELLUM • Hind brain- - small brain • Posterior cranial fosse • Forms roof of IV ventricle • Fissures and folia. 4. CEREBELLUM • Receives sensory data - Same side spinal cord - Dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar tract • Receives Motor data ...
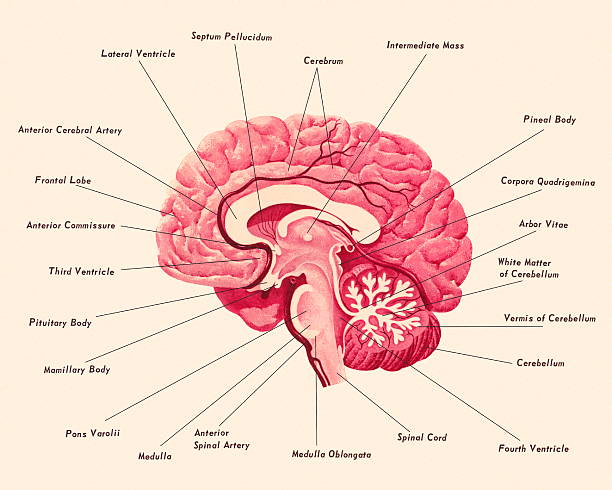
Midbrain - Wikipedia The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while caudally it adjoins the hindbrain (pons, medulla and cerebellum). In the rostral direction, the midbrain noticeably splays laterally. Sectioning of the midbrain is usually …
Sheep Brain Anatomy with Labeled Diagram - AnatomyLearner Here, the cerebral hemispheres (2), cerebellum, medulla oblongata, and colliculus are identified in the labeled diagram. Again, the diagram shows the cerebral gyrus and cerebral sulcus of the sheep brain. The 2 lateral lobes and single middle lobe of the sheep brain cerebellum are also identified in the labeled diagram.
The Cerebellum | Boundless Anatomy and Physiology | | Course Hero The cerebellum is separated from the overlying cerebrum by a layer of leathery dura mater. Anatomists classify the cerebellum as part of the metencephalon, which also includes the pons, and all its connections with other parts of the brain travel through the pons. The metencephalon is the upper part of the rhombencephalon, or hindbrain.
Histological Structure of Cerebellar Cortex - AnatomyLearner Cerebellum histology consists of outer gray matter and inner white matter in different animals. The outer gray matter of cerebellum found mainly the covering surface and known as cortex of cerebellum. On the other hand, white matter found in the central part of cerebellum and known as medulla of cerebellum.
Cerebellum - Anatomy, Structure, Function and Parts of the Brain - VEDANTU The cerebellum is a part of the brain of all vertebrates. The brain is the centre holding all necessary connections to all the sensory functions the body responds to. The brain can be considered to be a soft mass of connective tissues which also has nerves connected to the spinal cord that holds and supports the body.
Spinothalamic tract - Wikipedia There are two main parts of the spinothalamic tract: The lateral spinothalamic tract transmits pain and temperature.; The anterior spinothalamic tract (or ventral spinothalamic tract) transmits crude touch and firm pressure.; The spinothalamic tract, like the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway, uses three neurons to convey sensory information from the periphery to …
Graphics processing unit - Wikipedia A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed to manipulate and alter memory to accelerate the creation of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display device.GPUs are used in embedded systems, mobile phones, personal computers, workstations, and game consoles.. Modern GPUs are efficient at manipulating computer graphics and image …
Anatomy of the cerebellum - Wikipedia Gross anatomy. The cerebellum is located at the base of the brain, with the large mass of the cerebral cortex above it and the portion of the brainstem called the pons in front of it. It is separated from the overlying cerebrum by a layer of tough dura mater; all of its connections with other parts of the brain travel through the pons.Anatomists classify the cerebellum as part of the ...
Grey matter - Wikipedia Structure. Grey matter refers to unmyelinated neurons and other cells of the central nervous system.It is present in the brain, brainstem and cerebellum, and present throughout the spinal cord.. Grey matter is distributed at the surface of the cerebral hemispheres (cerebral cortex) and of the cerebellum (cerebellar cortex), as well as in the depths of the cerebrum (the thalamus; …
Lamprey - Wikipedia Lampreys / ˈ l æ m p r eɪ z / (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are an ancient extant lineage of jawless fish of the order Petromyzontiformes / ˌ p ɛ t r oʊ m ɪ ˈ z ɒ n t ɪ f ɔːr m iː z /, placed in the superclass Cyclostomata.The adult lamprey may be characterized by a toothed, funnel-like sucking mouth. The common name "lamprey" is probably derived from Latin …
Cerebellum: Functions, Structure, and Location - Simply Psychology The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain, behind the brainstem, below the temporal and occipital lobes, and beneath the back of the cerebrum. The cerebellum is also divided into two hemispheres, like the cerebral cortex. Unlike the cerebral hemispheres, each hemispheres of the cerebellum is associated with each side of the body.
Cerebellum labeled Diagram | Quizlet Cerebellum labeled + − Learn Test Match Created by nick_fontaine32 Terms in this set (11) Anterior lobe ... Primary fissure ... Posterior lobe ... Anterior Lobe (from below) ... Flocculus ... Nodule ... Posterior lobe (from below) ... Tonsil ... Vermis ... Paravermis ... Lateral hemisphere ... Sets found in the same folder Lab 4 Learning Objectives
Cell (biology) - Wikipedia Cell shapes. Cell shape, also called cell morphology, has been hypothesized to form from the arrangement and movement of the cytoskeleton. Many advancements in the study of cell morphology come from studying simple bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, E. coli, and B. subtilis. Different cell shapes have been found and described, but how and why cells form …
Join LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols;
Home Page: American Journal of Ophthalmology 9. lokak. 2022 · The American Journal of Ophthalmology is a peer-reviewed, scientific publication that welcomes the submission of original, previously unpublished manuscripts directed to ophthalmologists and visual science specialists describing clinical investigations, clinical observations, and clinically relevant laboratory investigations. More
Cerebellum: Gross anatomy and blood supply | Kenhub Origin and location The cerebellum arises from the rhombencephalon or hindbrain. More specifically, it arises from the rhombic lips or alar plates (dorsal thickening of the neural tube that forms the sensory areas of the nervous system) of the metencephalon (spans between the pontine flexure and the rhombencephalic isthmus).. It is an ovoid structure that resides in the posterior cranial fossa ...
Cerebellum Function, Anatomy & Definition | Body Maps - Healthline Cerebellum. The cerebellum is located behind the top part of the brain stem (where the spinal cord meets the brain) and is made of two hemispheres (halves). The cerebellum isn't unique to humans ...
Cerebellum Anatomy, Structure, Function, Pictures, Diagrams Cerebellum is located behind the right brain stem, in lower brain area. It has a large mass from the anterior cerebral cortex, and a portion of the brain stem. The cerebellum is divided into two hemispheres, and a cortex surrounding these hemispheres. The main function of the cerebellum is to organize the complex information received by the brain.
Cerebellum | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org The cerebellum is supplied by three bilateral arteries from the vertebrobasilar system: superior cerebellar artery (SCA): branch of the distal basilar artery. anterior inferior cerebellar (AICA): branch of the proximal basilar artery. posterior inferior cerebellar (PICA): branch of the distal vertebral arteries.
Cerebellum - Wikipedia The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. [1] In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control.
Cerebellum: histology, layers, cell types and anatomy | Kenhub Cerebellum (histological slide) The cerebellum, located dorsal to the pons and the medulla, is one of the primary structures of the hindbrain. It lies under the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. The cerebellum is an integral structure in transmitting sensory signals to the motor portion of the brain.
The Cerebellum - Structure - Position - Vasculature - TeachMeAnatomy The cerebellum, which stands for "little brain", is a structure of the central nervous system. It has an important role in motor control, with cerebellar dysfunction often presenting with motor signs. In particular, it is active in the coordination, precision and timing of movements, as well as in motor learning.
Nervous System - Label the Brain - TheInspiredInstructor.com Choose the correct names for the parts of the brain. ( 9) This brain part controls thinking. (10) This brain part controls balance, movement, and coordination. (11) This brain part controls involuntary actions such as breathing, heartbeats, and digestion. (12) This part of the nervous system moves messages between the brain and the body.
Cerebellum: Definition, Location, and Functions - Verywell Mind The cerebellum (which is Latin for "little brain") is a major structure of the hindbrain that is located near the brainstem. The cerebellum is the part of the brain that is responsible for coordinating voluntary movements. It is also responsible for a number of functions including motor skills such as balance, coordination, and posture.













:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/3449/z5HW6UK6VVwzeJnynMrpcA_cerebellum-inferior_english.jpg)










Post a Comment for "39 cerebellum labelled"